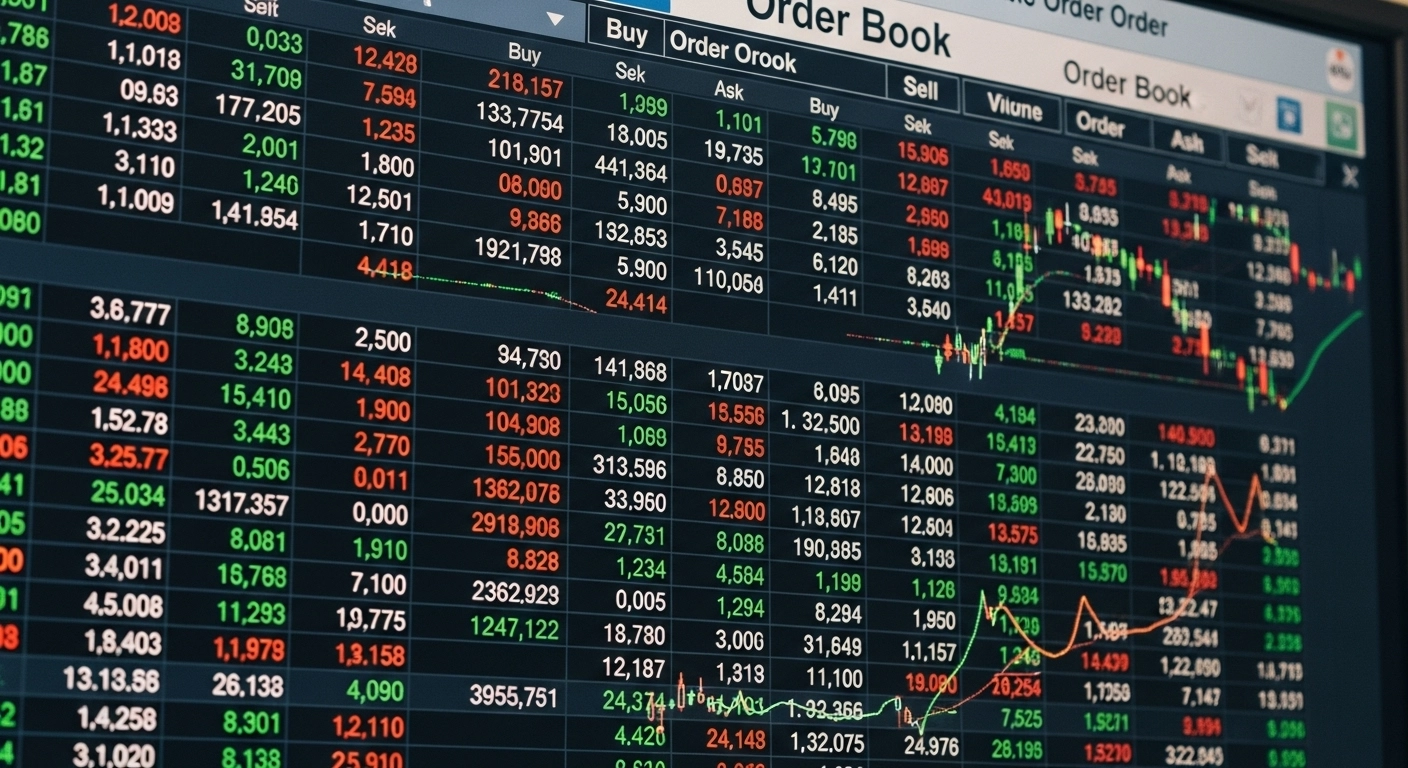
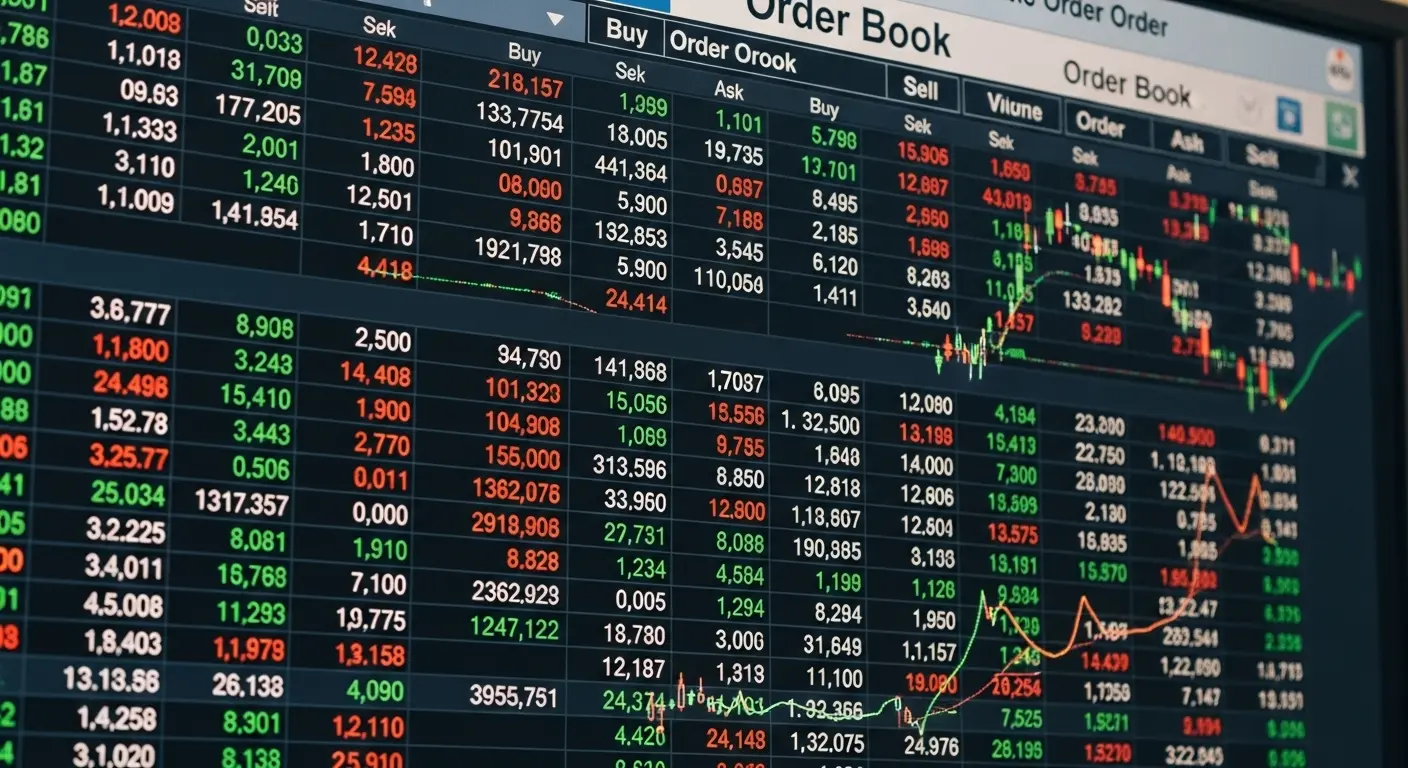
Building a Real-Time Order Book Simulator in Java
Trading systems and matching engines have always fascinated me — especially how exchanges juggle thousands of buy and sell orders in real time. So, I built a Java-based Order Book Simulator to model how markets actually work behind the scenes.
It runs on Java 21, with no dependencies, and simulates a full order flow: limit orders, market orders, matching, price updates, and even expiration logic. It even has a UI panel to visualize how the book moves.
What Does It Do?
- Matches limit and market orders in real time
- Tracks best bid/ask, mid price, and trade history
- Supports order expiration (to simulate time decay)
- Has a basic UI with live updates
- All built from scratch in Java
Here’s what it looks like in action:
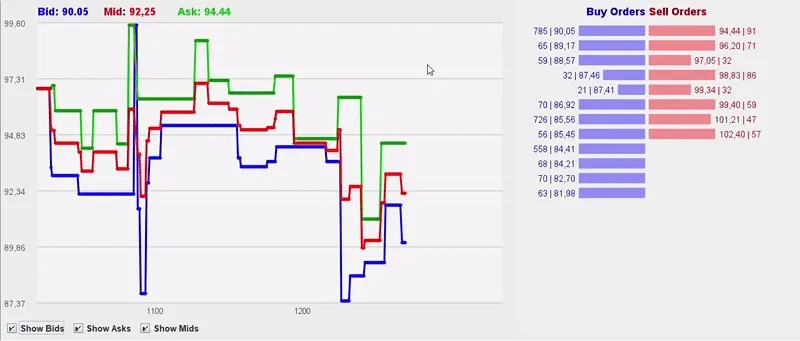
Peek Inside the Engine
In this blog post I will show you the important pieces to make this app work.
Project structure
src/├── com.afrancodev.orderbook/│ ├── OrderBookSimulator.java # Application entry point│ ├── SimulationEngine.java # Application main loop│ ├── OrderBook.java # Order management│ └── OrderGenerator.java # Random order generator│├── com.afrancodev.orderbook.models/│ ├── Order.java # Order representation| ├── Trade.java # Trade model│ ├── TradeHistory.java # Trade History model│ └── PriceLevelData.java # Aggregator of Prices and Quantities│├── com.afrancodev.orderbook.ui/│ ├── MainPanel.java # Main Ui Panel| ├── OrderBookPanel.java # Order Book Panel│ └── PriceChartPanel.java # Price Chart Panel🧠 SimulationEngine: The Heartbeat Loop
This method runs every tick of the simulation. It updates the fair price, generates a new random order, injects it into the book, and refreshes the UI:
private void engineLoop() { orderGenerator.updateFairPrice();
Order order = orderGenerator.generateRandomOrder(orderBook);
orderBook.addOrder(order); orderBook.matchOrders(); orderBook.updatePrices(); orderBook.expireOldOrders();
mainPanel.repaint();}Short and sweet. It’s the brain of the simulation.
🎲 OrderGenerator: Random Order Flow
This class simulates traders with randomized behavior. It chooses whether to place a market or limit order, whether to buy or sell, and what price/quantity to use — all based on configured probabilities.
public Order generateRandomOrder(OrderBook orderBook) { ThreadLocalRandom rand = ThreadLocalRandom.current();
boolean isBuy = rand.nextBoolean(); boolean isMarketOrder = rand.nextDouble() <= MARKET_ORDER_PROBABILITY;
double limitPrice; if (isMarketOrder) { Double bestBid = orderBook.getCurrentBid(); Double bestAsk = orderBook.getCurrentAsk(); limitPrice = isBuy ? (bestAsk != null ? bestAsk : fairPrice) : (bestBid != null ? bestBid : fairPrice); } else { double priceOffset = rand.nextDouble(0, SPREAD_WIDTH); limitPrice = isBuy ? fairPrice - priceOffset : fairPrice + priceOffset; }
boolean isLargeOrder = rand.nextDouble() < LARGE_ORDER_PROBABILITY; int quantity = isLargeOrder ? rand.nextInt(LARGE_ORDER_MIN, LARGE_ORDER_MAX) : rand.nextInt(SMALL_ORDER_MIN, SMALL_ORDER_MAX);
int age = rand.nextInt(MIN_AGE, MAX_AGE);
return new Order(isBuy, round(limitPrice), quantity, isMarketOrder, age);}By tweaking probabilities, you can simulate everything from stable markets to volatile chaos.
⚖️ OrderBook: Matching Engine Logic
Here’s the core of the exchange: matching orders using price-time priority. Market orders match immediately. Limit orders wait if they can’t cross the spread.
public void matchOrders() { synchronized (lock) { while (!buyOrders.isEmpty() && !sellOrders.isEmpty()) { Order buy = buyOrders.peek(); Order sell = sellOrders.peek();
if (buy.isMarketOrder() && sell.isMarketOrder()) { break; }
boolean canMatch = buy.isMarketOrder() || sell.isMarketOrder() || buy.getPrice() >= sell.getPrice(); if (!canMatch) { break; }
int tradedQty = Math.min(buy.getQuantity(), sell.getQuantity()); double tradePrice = determineTradePrice(buy, sell);
tradeHistory.recordTrade(new Trade(true, tradePrice, tradedQty));
buy.reduceQuantity(tradedQty); sell.reduceQuantity(tradedQty);
if (buy.getQuantity() == 0) { buyOrders.poll(); } if (sell.getQuantity() == 0) { sellOrders.poll(); } } }}It’s clean, thread-safe, and surprisingly satisfying to watch in motion.
Try It Yourself
You can run it with Java 21 + Maven:
mvn clean compile exec:javaNo libraries needed — just clone and run.
What’s Next?
Some ideas on the roadmap:
- 🕯️ Candlestick chart type
- ⏸️ Pause/resume simulation
- ⚙️ Settings panel (spread, speed, order size)
- 📊 Global metrics (order stats, time elapsed)
This project was a fun way to combine Java skills with a deeper understanding of how real markets work. If you’re curious about trading systems or building simulations, definitely give it a try.
Let me know what your suggestions or if you want you can fork it and make it your own. The code is on my github.
Happy Coding!
← Back to projects